The magnetron sputtering system has been in use for several decades now. Even recently, there have been advancements that have improved the performance of the sputtering system in general. For instance, the closed-field unbalanced magnetron sputtering technique has now been developed so that it can be routinely used to deposit high-quality coatings of an extensive range of materials.
Various Applications of Magnetron Sputtering System
Metals, alloys, ceramics, multi-layers, and functionally-graded materials can all be deposited with excellent structures and properties. In this post, you’ll learn more about magnetron sputtering applications.
Data Storage
Magnetron sputtering is used in several data storage devices. It can be used to manufacture DVDs, laser disks, hard disks, floppy disks, micro-electric flash memory, and CDs. It can also be used in the manufacture of nanostructured materials.
Defense
Magnetron sputtering is also used in the manufacture of defense equipment. It can be used to produce night vision equipment and mirrors for X-ray telescopes.
Wear Coatings
Sputtering is used to coat materials to extend the durability of the materials. Anti-corrosion coatings, anti-seize coatings, tools, and drill bit hardening, are processes in which the magnetron sputtering technique is used. Others include dies and molds, and sewing needles.
Electronics/Microelectronics
Electronics are another major application area where magnetron sputtering is extensively used. Manufacturers of electronic appliances use the sputtering technique to improve the durability of electronic parts. Magnetron sputtering is used in electronic appliances, such as gate dielectric, passive thin-film components, interlayer dielectric, sensors, printed circuit boards, and surface acoustic wave devices.
Decorations/Aesthetics
An important application of magnetron sputtering is in decorative projects, such as appliance trimming, glass building, jewelry making, packaging, plumbing fixtures, toys, and clothing items.
Automobiles
Another important application of magnetron sputtering is in the manufacture of automobiles. It is used in the production of headlights, taillights, auto trim components, wheels, and rims.
Aerospace and Defense
Aviation is another critical area where magnetron Sputtering is applied. Examples of parts where the sputtering techno is used in aerospace include heads-up cockpit displays, jet turbine engines, mirrors for optical and x-ray telescopes, night vision equipment, etc.
Optics
This includes anti-reflective coatings, cable communications, laser lenses, optical filters for achromatic lenses, and spectroscopy relies on magnetron sputtering technology. In this way, magnetron sputtering contributes to optics.
Jewelry
Magnetron sputtering is also used in making jewelry. It improves the overall appearance and quality of necklaces, rings, earrings, bracelets, cufflinks, anklets, and other accessories.

Medical Applications
Advanced magnetron sputtering is used in the medical field. Specific examples include the manufacture of angioplasty devices, anti-rejection coating, which prevents allergic reactions, radiation capsules, and dental implants.
Security
Magnetron sputtering is also relevant in security. Technological innovations like night vision, infrared equipment, one-way security windows, and currency holograms benefit from magnetron sputtering.
Energy
Magnetron sputtering plays an essential role in energy generation. Typical examples include gas turbine blade coating, outdoor display systems, signages, and solar panels.
Lighting
Lighting is another important application of magnetron sputtering: traffic signals, IR intensifiers, energy-efficient lighting, emission filters, and effectors.
Architectural Glass
Applications of magnetron sputtering also cut across architectural glass manufacturing. It is used in energy-producing glass, low-emissivity glass, and in building-integrated photovoltaics.
Plumbing Application
Magnetron sputtering is also applicable in coating plumbing fixtures. This helps to prevent corrosion and rusting in plumbing applications.
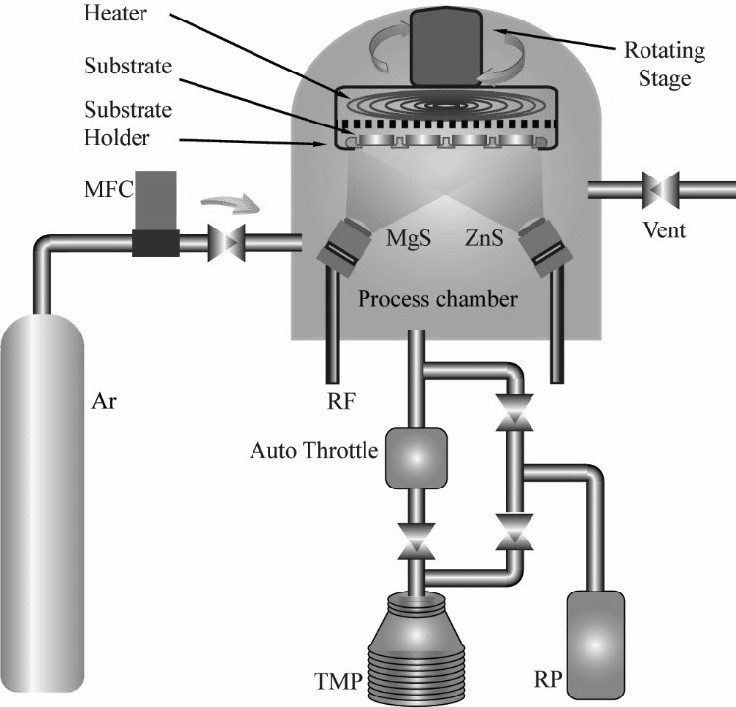
Significance of Magnetron Sputtering System
Magnetron sputtering is very versatile and can be used to apply just about any material. It is especially well suited to materials with a high melting point which would be difficult to melt in a normal vacuum thermal deposition system. It is often used for coating entire surfaces since it is difficult to control where the material goes precisely. Adhesion is therefore excellent.
Principle of Magnetron Sputtering System
Power is supplied to the magnetron, which produces a negative that is, in turn, applied to the sputtering target materials. This negative voltage then attracts positive ions to the target surface while simultaneously inducing large kinetic energy. The bombardment of the ions on the surface of the target leads to a transfer of energy.
Sputtering occurs if the energy transferred in a direction normal to the surface is larger than about three times the surface binding energy. This is approximately equal to the heat of sublimation. Also, the electrons travel for a longer distance, which increases the probability of further ionizing Argon atoms. This process generates a stable plasma with high ion density, making magnetron sputtering a preferred sputtering technique for the deposition of high-quality coatings.
Conclusion
Thank you for reading our article and we hope that it can help you better understand the applications of magnetron sputtering systems. If you want to know more about sputtering knowledge, we would like to advise you to visit Stanford Advanced Materials (SAM) for more information.