Introduction
Terbium sputtering targets are made from terbium metal. They are used widely in a range of sectors such as tool coatings, optics coatings, and solar coatings. Let’s have a detailed discussion about the features, production, and applications of terbium sputtering targets.
Properties
Terbium sputtering targets share similar features with terbium metal.
- Terbium the element (Tb, 65) is located in Group 3, Period 6 of the periodic table. It is a silver-white soft metal with a melting point of 1,356°C and a boiling point of around 2,800°C. You can check the table below to learn more about terbium’s physical features.
- In terms of chemical class, terbium is a rare earth element belonging to the lanthanide series. Terbium is electropositive, so it easily oxides. It reacts with water slowly in the air and dissolves in acids. Additionally, the compounds of terbium are highly fluorescent and used in various industries.
Table 1 Terbium Sputtering Targets Specifications
| Material Type | Terbium-Metal |
| Symbol | Tb |
| Atomic Weight | 158.92535 |
| Atomic Number | 65 |
| Color/Appearance | Silvery White, Metallic |
| Melting Point (°C) | 1356 |
| Boiling Point (°C) | 2800 |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion | 10.3 x 10-6/K |
| Density (g/cm3) | 8.33 |
| Available Sizes | Dia.: 1.0″, 2.0″, 3.0″, 4.0″
Thick: 0.125″, 0.250″ |
Further reading: Rare Earth Terbium – Element Information
Manufacturing Process
Get Purified Terbium
The manufacturing process of terbium sputtering targets starts from the production of pure metal terbium. Although terbium is quite abundant in the Earth’s crust, it is not found as a free element in nature. Terbium is extracted from minerals like cerite, gadolinite, monazite, and euxenite. You need to separate the metal from its rare-earth cousins.
Ion exchange and valency change are two techniques that are frequently used to get pure lanthanides. As for terbium, the former method is preferred.
From Terbium to Terbium Target
– Casting
The casting process can be divided into three steps: melting, casting, and machining.
- You need to melt the raw terbium to a certain distribution ratio initially.
- Next, pour them into the mold to form a terbium ingot.
- Finally, get the terbium sputtering target through the designed machining. Metallic targets could be machined into the appropriate shape suited to the sputtering system.
- Make sure the process is performed in a vacuum or inert atmosphere to prevent oxidation
Figure 1. shows the manufacturing process of the titanium sputtering target. The casting process is similar to that of terbium targets.

Further Reading: An Introduction to Metal Casting Process
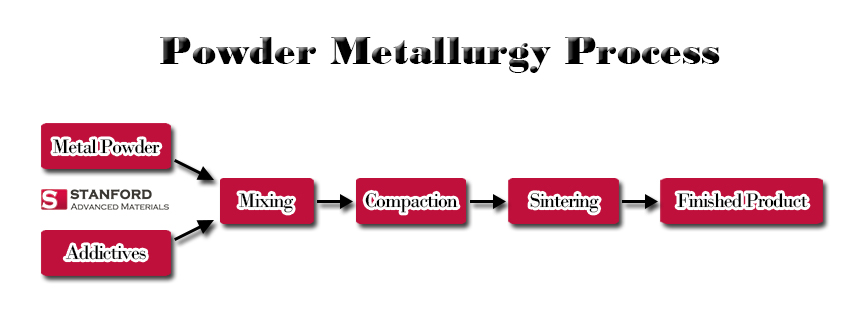
– Powder metallurgy
You can choose powder metallurgy if you can’t get the expected target dimensions through casting.
- Similar to the casting method, the powder metallurgy process starts from melting and casting.
- Then, you need to pulverize them and press the powder.
- Quality terbium sputtering targets are obtained ultimately through sintering at a high temperature.
Figure 2. shows the general process of powder metallurgy.
Applications
- Terbium sputtering materials are applied for decoration, functional coatings, flat panel displays, and so on.
- Terbium metal serves as an important additive for Nd-Fe-B permanent magnets to improve their performance. The metal is also used as a dopant in calcium fluoride and calcium tungstate. You can also find terbium in laser devices and naval sonar systems.
- A majority of terbium compounds are used to make green phosphors in fluorescent lamps and color television tubes.
Conclusion
Terbium sputtering targets come from silvery malleable terbium metal. You can obtain these sputtering materials for the coating industry by casting and powder metallurgy. Hope that you can get a better understanding of terbium sputtering targets after reading this article. Terbium sputtering targets of different sizes, shapes, and prices are available at Stanford Advanced Materials. Check our homepage for more information.





