| Purity | 99.9% |
| Theoretical Density | 7.353 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 1072 ℃ |
| Boiling Point | 1791 °C |
| Product Shape | Rectangular, or customized upon request |
| Product Size | Customized |
Stanford Advanced Materials (SAM) offers high-purity Samarium (Sm) Planar Sputtering Targets designed for thin-film deposition applications requiring strong magnetic properties, thermal stability, and oxidation resistance. Samarium is a rare-earth metal with a melting point of 1,072°C and naturally forms a protective oxide layer, making it well-suited for reactive or high-temperature environments.
SAM’s samarium targets are produced with a fine-grained microstructure for consistent sputtering and uniform film deposition. Available in purities ranging from 99.9% to 99.99% and customizable in size and shape, these targets support advanced applications including magneto-optical storage, microelectronics, and high-performance protective coatings.
Properties
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Theoretical Density | 7.353 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 1072 ℃ |
| Boiling Point | 1791 °C |
| Product Shape | Rectangular, or customized upon request |
| Product Size | Customized |
*The above product information is based on theoretical data. For specific requirements and detailed inquiries, please contact us.
Magnetic Thin Films & Magneto-Optical Storage
Used in MO disks, optical isolators, MRAM, and spintronics
Offers strong magneto-optical effects and magnetic stability
Semiconductors & Microelectronics
Enables Sm-based films for Hall sensors, magnetoresistive devices
Functions as a barrier or protective coating layer
Optical Coatings
Suitable for infrared optics, laser mirrors, and AR coatings
Low IR absorption, high durability
Wear-Resistant & Protective Coatings
Applied to aerospace parts, industrial tools
Improves hardness, corrosion, and oxidation resistance
Research & Emerging Technologies
Used in Sm-containing superconducting compounds (e.g., SmFeAsO)
Applied in neutron shielding coatings for nuclear materials
Small Targets: PP boxes with anti-static and moisture protection
Large or Custom Targets: Custom wooden crates with interior cushioning
All shipments follow strict packaging protocols to prevent damage during transit
Packaging Options: Carton, Wooden Crate, or Fully Customized
Other shapes: Samarium Sputtering Target
Related Products: Samarium Nickel Oxide Sputtering Target, Samarium Oxide Sputtering Target, Samarium Fluoride Sputtering Target
1. Brief Manufacturing Process Flow
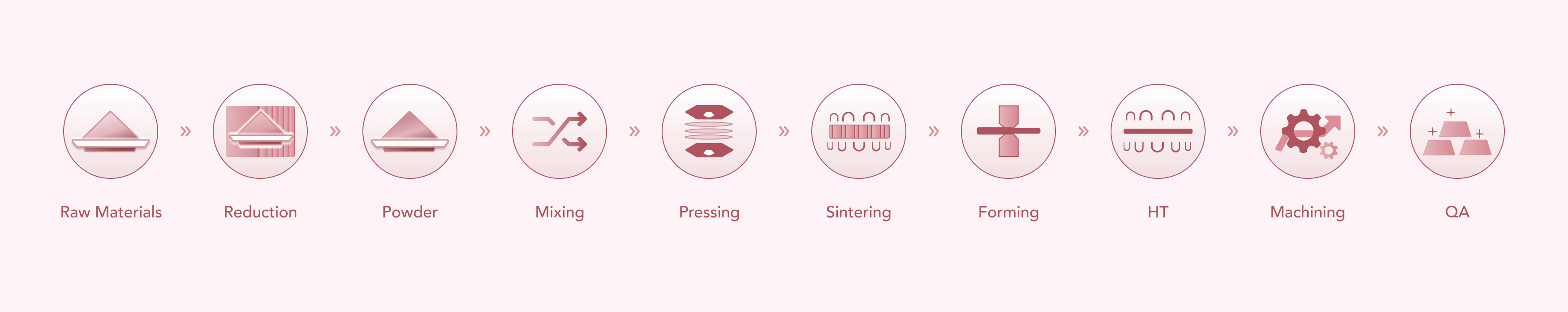 2. Testing Method
2. Testing Method
Chemical Analysis – GDMS or XRF used to verify purity
Mechanical Testing – Measures tensile strength, yield, and elongation
Dimensional Inspection – Confirms target dimensions meet tolerance
Surface Inspection – Visual and ultrasonic checks for defects
Hardness Testing – Assesses consistency in material hardness
Q1: Can you produce custom dimensions or shapes?
A1: Yes. We offer target diameters from 50–200 mm, thicknesses from 3–10 mm, and optional Cu/Ag bonding.
Q2: What’s the expected service life of a samarium planar target?
A2: With proper sputtering conditions, our fine-grain (<50 µm) targets achieve over 85% utilization under standard DC/RF sputtering.
Q3: How should the targets be stored and handled?
A3: Store in a dry, inert gas (argon/nitrogen) atmosphere. Use gloves to avoid contamination. Pre-sputter cleaning is recommended.
Samarium Rotary Target vs. Samarium Planar Target
| Feature | Samarium Rotary Target | Samarium Planar Target |
|---|---|---|
| Material Use | Up to 80–90% | Around 30–40% |
| Service Life | Longer | Shorter |
| Coating Uniformity | High, better for large areas | May vary across the surface |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher initial, lower long-term | Lower upfront, more replacements |
| Applications | Large-area coatings | Small-area precision coatings |
| Sputtering Stability | More stable erosion | Less stable, risk of uneven wear |
| Equipment Type | Rotary sputtering systems | Planar sputtering systems |
Atomic Number: 62
Atomic Weight: 150.36
Density: 7.353 g/cm³
Melting Point: 1,072°C
Boiling Point: 1,791°C
Samarium is moderately hard, brittle, and forms an oxide layer in air that enhances corrosion resistance. It is typically sourced from minerals like monazite and bastnäsite.
Key Applications:
Magnets: Key component in SmCo permanent magnets with high thermal resistance
Optics & Electronics: Infrared absorption, laser and display materials
Nuclear & Ceramics: Neutron-absorbing coatings, specialty glass, and ceramics
Samarium’s thermal stability, magnetic strength, and chemical resistance make it vital in precision coating systems and advanced material development.