| Purity | 99.9% |
| Theoretical Density | 6.77 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 935 °C |
| Boiling Point | 3520°C |
| Product Size | Customized |
Stanford Advanced Materials (SAM) supplies high-purity Praseodymium Planar Targets for thin-film deposition. Praseodymium is a rare-earth metal with a silvery appearance and a melting point of 931°C. It forms a stable oxide layer in air, giving it excellent resistance to oxidation and environmental degradation—ideal for coatings exposed to heat and reactive conditions.
Known for its magnetic, optical, and electrical characteristics, praseodymium enhances film performance in a range of applications. Its fine grain structure and purity support uniform deposition and consistent sputtering results. SAM offers praseodymium targets in various purities and dimensions to meet system and project specifications.
Properties
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Theoretical Density | 6.77 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 935 °C |
| Boiling Point | 3520°C |
| Product Size | Customized |
*The above product information is based on theoretical data. For specific requirements and detailed inquiries, please get in touch with us.
Electronics & Semiconductors – Used in dielectric and insulating layers for microelectronics.
Optical Coatings – Applied to high-performance lenses, filters, and laser systems.
Magnetic Storage – Supports advanced magnetic film technologies.
Energy Systems – Found in films for fuel cells and catalytic converters.
Industrial Coatings – Used in ceramic coatings, protective films, and aerospace materials.
Products are packaged based on size and fragility:
Small components: Sealed in PP boxes
Larger items: Secured in custom wooden crates
All packages include protective cushioning to prevent damage during transport.
Packaging options: Carton, wooden crate, or customized per order.
Other shapes: Praseodymium Sputtering Target
Related Products: Praseodymium Fluoride Sputtering Target, Praseodymium Nickel Oxide Sputtering Target, Praseodymium Oxide Sputtering Target, Praseodymium Cerium Manganate Sputtering Target
1. Brief Manufacturing Process Flow
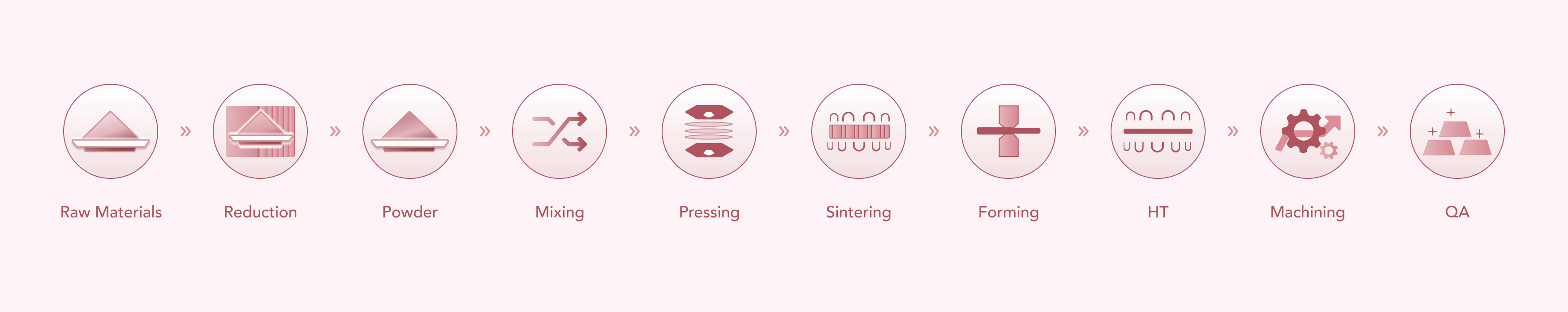 2. Testing Method
2. Testing Method
Chemical Analysis – GDMS or XRF used to verify purity
Mechanical Testing – Measures tensile strength, yield, and elongation
Dimensional Inspection – Confirms target dimensions meet tolerance
Surface Inspection – Visual and ultrasonic checks for defects
Hardness Testing – Assesses consistency in material hardness
Q1: What makes praseodymium suitable for thin-film coatings?
A1: Its oxidation resistance, thermal stability, and unique magnetic/optical properties improve coating performance and durability.
Q2: Where are praseodymium sputtering targets used?
A2: In electronics, semiconductors, optics, magnetic storage, fuel cells, and high-performance ceramics.
Q3: Can praseodymium targets be customized?
A3: Yes. We offer custom sizes, shapes, and bonding formats to meet different equipment and project needs.
Praseodymium Rotary Target vs. Praseodymium Planar Target
| Feature | Praseodymium Rotary Target | Praseodymium Planar Target |
|---|---|---|
| Material Use | 80–90% | 30–40% |
| Service Life | Longer | Shorter |
| Uniformity | High, ideal for large areas | May vary across surface |
| Cost Efficiency | Better long-term value | Lower upfront cost |
| Applications | Displays, solar, optics | Semiconductors, precision |
| Stability | More stable sputtering | May erode unevenly |
| System Use | Rotary sputtering systems | Planar sputtering systems |
Atomic Number: 59
Atomic Weight: 140.91
Density: 6.77 g/cm³
Melting Point: 931°C
Boiling Point: 3,520°C
Praseodymium is reactive with oxygen but forms a stable oxide layer that protects it from further corrosion. It is extracted from rare-earth minerals like monazite and bastnäsite.
Uses:
Magnets and Alloys – Improves strength and magnetism
Lasers and Optics – Used in praseodymium-doped glass
Energy and Ceramics – Applied in fuel cells, catalytic films, and structural coatings
Its thermal stability, corrosion resistance, and unique functional properties make praseodymium valuable in advanced material development.