| Grade | Density
(g/cm3) |
Average Grain Size
(μm) |
Roughness
(μm) |
Straightness
(mm) |
Bonding Rate |
| MoNb5 | ≥10.00 | ≤100 | ≤0.8 | ≤0.30 | ≥97% |
| MoNb10 | ≥9.90 | ≤100 | ≤0.8 | ≤0.30 | ≥97% |
Stanford Advanced Materials (SAM) supplies Molybdenum-Niobium (MoNb) alloy rotary targets for thin-film deposition in high-demand environments. The standard alloy contains 90% molybdenum and 10% niobium, combining molybdenum’s thermal and electrical conductivity with niobium’s added mechanical strength and corrosion resistance.
MoNb rotary targets allow for high material utilization (up to 80–90%), which extends target lifespan and reduces production downtime. The uniform grain structure and controlled composition ensure stable sputtering and even coating across large surfaces.
These targets are available in a range of dimensions and can be tailored to fit different sputtering systems. SAM manufactures and inspects each target to meet strict quality and performance standards.
Properties
| Grade | Density
(g/cm3) |
Average Grain Size
(μm) |
Roughness
(μm) |
Straightness
(mm) |
Bonding Rate |
| MoNb5 | ≥10.00 | ≤100 | ≤0.8 | ≤0.30 | ≥97% |
| MoNb10 | ≥9.90 | ≤100 | ≤0.8 | ≤0.30 | ≥97% |
Chemical Composition. %
| Chemical Composition | MoNb5 | MoNb10 | |
| Main Content, %, min
Mo |
Mo | 94.85-95.05 | 89.85-90.05 |
| Nb | 5.00±0.1 | 10.00±0.1 | |
| Impurity Content (mass fraction),
%, max |
Al | 0.0050 | 0.0050 |
| Cr | 0.0050 | 0.0050 | |
| Cu | 0.0050 | 0.0050 | |
| Fe | 0.0100 | 0.0100 | |
| Ni | 0.0050 | 0.0050 | |
| Si | 0.0060 | 0.0060 | |
| C | 0.0150 | 0.0150 | |
| O | 0.0800 | 0.0800 | |
| N | 0.0300 | 0.0300 | |
*The above product information is based on theoretical data. For specific requirements and detailed inquiries, please get in touch with us.
Other shapes: Molybdenum Niobium Alloy Planar Target
Related Products: Molybdenum Rhenium Sputtering Target, Molybdenum Disilicide Sputtering Target, Molybdenum Silicon Sputtering Target, Molybdenum Selenide Sputtering Target, Molybdenum Boride Sputtering Target
Products are packaged based on size and fragility:
1. Brief Manufacturing Process Flow
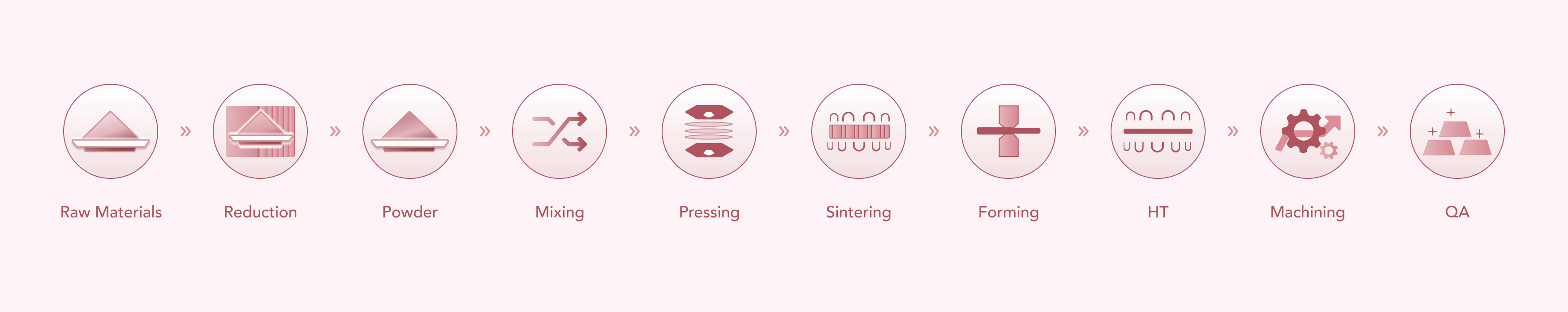
2. Testing Method
Chemical Analysis: GDMS or XRF for purity.
Mechanical Testing: Tensile strength, yield, elongation.
Dimensional Inspection: Ensures specs are met.
Surface Quality Check: Visual and ultrasonic inspection for defects.
Hardness Testing: Verifies material integrity.
Q1: Why choose rotary targets over planar?
A1: They use more of the material (up to 80–90%) and last longer, which cuts down on replacements and waste. Further reading: Planar Targets VS. Rotatory Targets
Q2: Where are MoNb rotary targets used?
A2: In applications requiring reliable, high-performance films: displays, semiconductors, solar cells, and corrosion-resistant coatings.
Q3: What does niobium add to molybdenum targets?
A3: Niobium improves resistance to oxidation and corrosion, and boosts mechanical durability, especially under thermal and chemical stress.
MoNb Rotary vs. MoNb Planar Target
| Feature | MoNb Rotary Target | MoNb Planar Target |
|---|---|---|
| Material Use | 80–90% | 30–40% |
| Service Life | Longer | Shorter |
| Coating Uniformity | Higher, better for large areas | Less consistent |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher initial, lower long-term | Lower initial, more frequent replacements |
| Equipment | Rotary sputtering systems | Traditional planar systems |
| Ideal Use | Large-area coatings | Small-area, precision coatings |
Atomic Number: 42
Density: 10.28 g/cm³
Melting Point: 2,617°C
Thermal Conductivity: 138 W/m·K
Used in electronics, high-temp alloys, energy systems, and as a catalyst in refining.
Atomic Number: 41
Density: 8.57 g/cm³
Melting Point: 2,477°C
Thermal Conductivity: 53.7 W/m·K
Used in superconductors, aerospace, energy systems, and corrosion-resistant equipment.