| Grade | Density
(g/cm3) |
Average Grain Size
(μm) |
Roughness
(μm) |
Straightness
(mm) |
Bonding Rate |
| MoNb5 | ≥10.00 | ≤100 | ≤0.8 | ≤0.30 | ≥97% |
| MoNb10 | ≥9.90 | ≤100 | ≤0.8 | ≤0.30 | ≥97% |
Stanford Advanced Materials (SAM) supplies Molybdenum-Niobium (MoNb) alloy planar targets engineered for high-performance thin-film deposition. Typically made with 90% molybdenum and 10% niobium, this alloy combines molybdenum’s high thermal and electrical conductivity with niobium’s added strength and corrosion resistance.
Targets are available in a range of purity grades (99.9% to 99.999%) and formats, including plates, discs, and custom shapes to fit various sputtering systems. The niobium content improves resistance to oxidation and alkali corrosion, making MoNb well-suited for demanding deposition environments.
With tight grain control and uniform alloying, SAM’s MoNb targets support strong adhesion and consistent film quality. Each target is produced under strict quality control and can be tailored to meet specific application or equipment requirements.
Properties
| Grade | Density (g/cm³) | Avg. Grain Size (μm) | Surface Roughness (μm) | Straightness (mm) | Bonding Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MoNb5 | ≥10.00 | ≤100 | ≤0.8 | ≤0.30 | ≥97 |
| MoNb10 | ≥9.90 | ≤100 | ≤0.8 | ≤0.30 | ≥97 |
Chemical Composition. %
| Chemical Composition | MoNb5 | MoNb10 | |
| Main Content, %, min
Mo |
Mo | 94.85-95.05 | 89.85-90.05 |
| Nb | 5.00±0.1 | 10.00±0.1 | |
| Impurity Content (mass fraction),
%, max |
Al | 0.0050 | 0.0050 |
| Cr | 0.0050 | 0.0050 | |
| Cu | 0.0050 | 0.0050 | |
| Fe | 0.0100 | 0.0100 | |
| Ni | 0.0050 | 0.0050 | |
| Si | 0.0060 | 0.0060 | |
| C | 0.0150 | 0.0150 | |
| O | 0.0800 | 0.0800 | |
| N | 0.0300 | 0.0300 | |
*The above product information is based on theoretical data. For specific requirements and detailed inquiries, please get in touch with us.
Other shapes: Molybdenum Niobium Alloy Rotary Target
Related Products: Molybdenum Rhenium Sputtering Target, Molybdenum Disilicide Sputtering Target, Molybdenum Silicon Sputtering Target, Molybdenum Selenide Sputtering Target, Molybdenum Boride Sputtering Target
Flat Panel Displays & Touch Panels – Improves electrode layer performance and adhesion in TFT-LCD and OLED manufacturing.
Semiconductors & Microelectronics – Used as a barrier or adhesion layer in ICs and other microelectronic devices.
Optical Coatings – Adds durability and clarity to anti-reflective and functional optical films.
Thin-Film Solar Cells (CIGS) – Provides stable back contacts for efficient energy conversion.
Corrosion-Resistant Coatings – Performs well in high-alkali and oxidative environments.
Packaging is based on product size and type:
1. Brief Manufacturing Process Flow
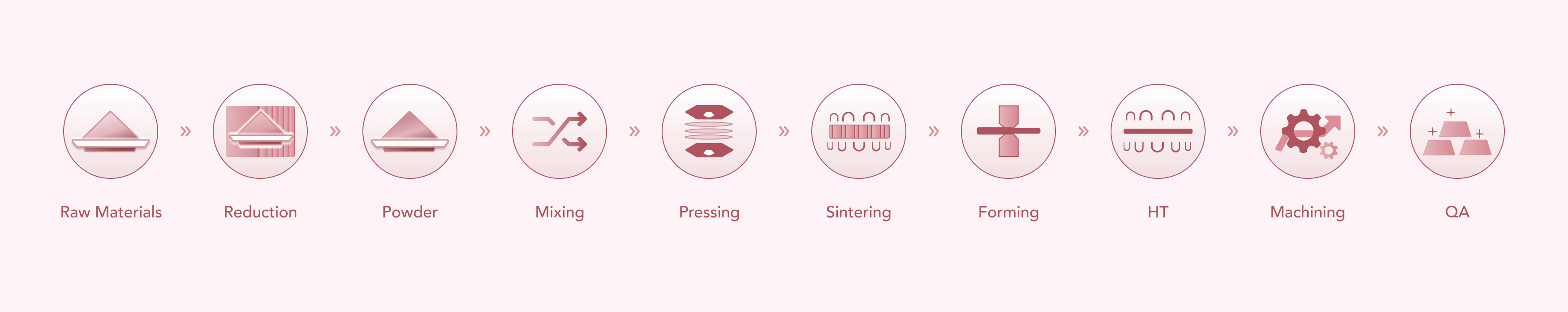
2. Testing Method
Chemical Analysis – Verified by GDMS or XRF
Mechanical Testing – Tensile, yield, and elongation measurements
Dimensional Inspection – Ensures target thickness, width, and length are within spec
Surface Quality Check – Detects cracks, voids, and inclusions via visual and ultrasonic tools
Hardness Testing – Confirms consistency and mechanical reliability
Q1: Why use MoNb instead of pure molybdenum?
A1: Niobium improves corrosion resistance, oxidation resistance, and mechanical durability, especially in high-temperature or chemically aggressive environments.
Q2: Where are MoNb planar targets used?
A2: In display tech, semiconductors, optics, solar cells, and any environment needing stable, corrosion-resistant films.
Q3: How should MoNb targets be stored?
A3: Store in a clean, dry space. Avoid contact with moisture and handle carefully to prevent contamination or surface damage.
Molybdenum Niobium Rotary Target vs. Molybdenum Niobium Planar Target
| Feature | Rotary Target | Planar Target |
|---|---|---|
| Material Use | 80–90% | 30–40% |
| Service Life | Longer | Shorter |
| Film Uniformity | High, good for large areas | May vary across surface |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher initial, better ROI | Lower upfront, more changes |
| Applications | Displays, solar, optics | Chips, sensors, small areas |
| Sputter Stability | High | Lower |
| Equipment | Rotary sputtering systems | Planar sputtering systems |
Molybdenum (Mo)
High melting point (2,617°C)
Strong thermal and electrical conductivity
Good corrosion resistance
Common in coatings, electronics, energy systems, and structural alloys
Niobium (Nb)
Melting point: 2,477°C
Strong oxidation and alkali resistance
Excellent mechanical strength
Used in superconductors, aerospace alloys, and chemical-resistant components
The MoNb alloy benefits from the best of both elements: thermal and electrical performance from molybdenum, mechanical resilience and corrosion resistance from niobium.